
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
HEAO
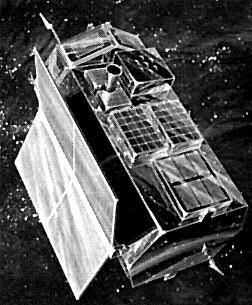 HEAO Credit: NASA |
AKA: High Energy Astronomical Observatory. Status: Operational 1977. First Launch: 1977-08-12. Last Launch: 1979-09-20. Number: 3 . Gross mass: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb). Height: 9.00 m (29.50 ft).
HEAO 1 was primarily a survey mission, dedicated to systematically mapping the X-ray sky every 6 months. HEAO 1 performed almost 3 full celestial surveys and discovered 1500 new X-ray sources. HEAO 2 (also named Einstein) was the world's first orbiting imaging X-ray telescope and returned detailed quasar images and discovered that Jupiter and Earth emit X-rays. The satellite also made over 5,000 targeted observations and discovered several thousand "serendipitous" sources that fell within the field of view of its imaging instruments. HEAO-3 was designed to detect cosmic ray particles and gamma-ray photons to further the understanding of the strength and extent of interstellar magnetic fields, the distribution of interstellar matter, and the stellar nucleosynthesis process which has created the heavy elements contained in most ordinary matter. All three of the High Energy Astronomy Observatories were regarded as highly successful. The total cost of the program was about $250 million. HEAO 1 re-entered 3/15/79, HEAO 2 re-entered 3/25/82, and HEAO 3 re-entered 12/7/81.
The spacecraft was 3-axis stabilized. Fixed solar panels generated 600 watts and recharged NiCd batteries (24 AHr). The aluminum honeycomb structure used passive thermal control. The hydrazine propulsion system had 110 kg fuel and 6 dual thrusters. S-Band communications used omni antennas. The attitude control system provided arcminute pointing accuracy and arcsecond attitude determination.
Payloads for HEAO 1 were:
- A1 - Large Area Sky Survey experiment (LASS) - covered the energy range 0.25 to 25.0 keV
- A2 - Cosmic X-ray Experiment (CXE) - designed to study the large scale structure of the galaxy and the universe, yielding high quality spatial and spectral data over the energy range 2-60 keV
- A3 - Modulation Collimator (MC) - designed to measure positions of X-ray sources with sufficient precision to identify optical and/or radio counterparts
- A4 - Hard X-Ray / Low Energy Gamma Ray Experiment.
HEAO 2 carried an X-ray telescope sensitive over the approximate energy range 0.2-3.5 keV. The telescope focused energy on one of four instruments:
- High Resolution Imaging (HRI) - a digital X-ray camera which provided high spatial and temporal resolution in the 0.15-3.0 keV energy range
- Imaging Proportional Counter (IPC) - a position sensitive proportional counter sensitive between 0.4-4.0 keV
- Solid State Spectrometer (SSS) - a cryogenically cooled lithium-drifted Si(Li) detector with a range between 0.5-4.5 keV
- Bragg crystal spectrometer (FPCS)
. HEAO-2 also carried the Monitor Proportional Counter (MPC), which monitored the 1-20 keV X-ray flux of the sources being observed by the telescope, as well as a Broad Band Filter (BBFS) spectrometer and an Objective Grating Spectrometer (OGS).
HEAO 3 carried a gamma ray spectrometer with 4 cryogenically cooled germanium detectors, each with an energy range of 50 keV to 10 MeV.
More at: HEAO.
| HEAO 2 (Einstein) Null |
| HEAO 3 Astronomy, X-Ray, Gamma satellite built by TRW for NASA, USA. Launched 1979. Used HEAO Bus. |
Family: Astronomy, Medium earth orbit, X-ray astronomy satellite. Country: USA. Launch Vehicles: Atlas, Atlas SLV-3D Centaur. Launch Sites: Cape Canaveral, Cape Canaveral LC36B. Agency: NASA, NASA Huntsville. Bibliography: 2, 278, 279, 6, 6551, 12528, 12529, 12530.
 | HEAO 1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | HEAO 2 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | HEAO 3 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
1973 Feb - . LV Family: Titan. Launch Vehicle: Titan IIIC.
- Large HEAO satellite split into three smaller spacecraft. - . Spacecraft: HEAO. NASA cancelled Air Force procurement of a Titan IIIC launch vehicle for the planned 1975 launch of its High Energy Astronomy Observatory (HEAO) satellite (cancelled in favor of smaller satellites)..
1977 August 12 - . 06:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- HEAO 1 - . Payload: HEAO A. Mass: 2,720 kg (5,990 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Huntsville. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: HEAO. Decay Date: 1979-03-15 . USAF Sat Cat: 10217 . COSPAR: 1977-075A. Apogee: 447 km (277 mi). Perigee: 429 km (266 mi). Inclination: 22.70 deg. Period: 93.40 min. High Energy Astronomical Observatory; surveyed sky in X-ray band. Spacecraft engaged in research and exploration of the upper atmosphere or outer space (US Cat B)..
1978 November 13 - . 05:24 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- HEAO 2 - . Payload: HEAO B. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA Huntsville. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: HEAO. Decay Date: 1982-03-25 . USAF Sat Cat: 11101 . COSPAR: 1978-103A. Apogee: 548 km (340 mi). Perigee: 526 km (326 mi). Inclination: 23.50 deg. Period: 95.40 min. High Energy Astronomy Observatory. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C)..
1979 September 20 - . 05:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC36B. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas SLV-3D Centaur.
- HEAO 3 - . Payload: HEAO C. Mass: 3,150 kg (6,940 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: NASA. Class: Astronomy. Type: X-ray astronomy satellite. Spacecraft: HEAO. Decay Date: 1981-12-07 . USAF Sat Cat: 11532 . COSPAR: 1979-082A. Apogee: 503 km (312 mi). Perigee: 487 km (302 mi). Inclination: 43.60 deg. Period: 94.50 min. High Energy Astronomy Observatory; cosmic, gamma ray measurements. Spacecraft engaged in practical applications and uses of space technology such as weather or communication (US Cat C)..
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use