
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Nitric acid/Hydrazine
Nitric acid/Hydrazine propellant. Problems which caused the abandoning of this propellant combination were the absence of reliable hypergolic ignition and unstable combustion. IRFNA (inhibited red fuming nitric acid)/UDMH and IRFNA/JP-X finally did prove satisfactory. No rocket engines with this propellant combination entered production.
Specific impulse: 328 s. Specific impulse sea level: 283 s. Location: 1725.
Optimum Oxidizer to Fuel Ratio: 1.45. Temperature of Combustion: 3,045 deg K. Ratio of Specific Heats: 1.25. Density: 1.28 g/cc. Characteristic velocity c: 1,725 m/s (5,659 ft/sec). Isp Shifting: 283 sec. Isp Frozen: 277 sec. Mol: 20.00 M (65.00 ft). Oxidizer Density: 1.510 g/cc. Oxidizer Freezing Point: -42 deg C. Oxidizer Boiling Point: 86 deg C. Fuel Density: 1.008 g/cc. Fuel Freezing Point: 2.00 deg C. Fuel Boiling Point: 113 deg C.
Subtopics
 | 1956 Von Braun Cargo Ship American manned Mars orbiter. Study 1956. Using the same basic systems as the Passenger Ship, the Cargo Ship would substitute a 177 metric ton Landing Boat for the surface expedition in place of the Passenger Sphere and propellant for the return home. |
 | 1956 Von Braun Landing Boat American manned Mars lander. Study 1956. The 1956 modification of Von Braun's Landing Boat design was reduced in mass by 12%, and the wingspan by 10%. |
 | 1956 Von Braun Passenger Ship American manned Mars orbiter. Study 1956. The 1956 version of Von Braun's Mars design was slashed by 50% in mass, while the number of passengers was increased from 10 to 12. |
 | Progress Russian logistics spacecraft. Progress took the basic Soyuz 7K-T manned ferry designed for the Salyut space station and modified it for unmanned space station resupply. Cargo satellite operated by RKK, Russia. Launched 1978 - 1990. |
| Progress PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 43 launches, 1978.01.20 (Progress 1) to 1990.05.06 (Progress 42). Derived from Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
 | Salyut 1 Russian manned space station. Salyut 1 was the first DOS long duration orbital station, an Almaz spaceframe modified with Soyuz systems by a joint Korolev-Chelomei team. Launched 1971. |
 | Salyut 4 Russian manned space station. Four of the initial DOS-1 versions of a civilian Soviet space station were built using converted Almaz military stations. Launched 1973. |
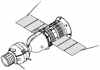 | Soyuz 7K-MF6 Russian manned spacecraft. Soyuz 22. Soyuz 7K-T modified with installation of East German MF6 multispectral camera. Used for a unique solo Soyuz earth resources mission. Launched 1976. |
| Soyuz 7K-MF6 PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. One launch, 1976.09.15, Soyuz 22. Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
 | Soyuz 7K-OK Russian manned spacecraft. Development of a three-manned orbital version of the Soyuz, the 7K-OK was approved in December 1963. Launched 1966 - 1969. |
| Soyuz 7K-OK PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 17 launches, 1966.11.28 (Cosmos 133) to 1970.06.01 (Soyuz 9). Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
| Soyuz 7K-OKS PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 2 launches, 1971.04.23 (Soyuz 10) to 1971.06.06 (Soyuz 11). Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
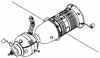 | Soyuz 7K-T Russian manned spacecraft. Launched 1972 - 1981. |
| Soyuz 7K-T PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 23 launches, 1972.06.26 (Cosmos 496) to 1981.05.14 (Soyuz 40). Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
 | Soyuz 7K-T/A9 Russian manned spacecraft. Version of 7K-T for flights to Almaz. Known difference with the basic 7K-T included systems for remote control of the Almaz station and a revised parachute system. Russian orbital launch vehicle variant. |
 | Soyuz 7K-TM Russian manned spacecraft. The Soyuz 7K-T as modified for the docking with Apollo. Launched 1974 - 1975. |
 | Soyuz 7KT-OK Russian manned spacecraft. This was a modification of Soyuz 7K-OK with a lightweight docking system and a crew transfer tunnel. Launched 1971. |
 | Soyuz A Russian manned spacecraft. Study 1962. The 7K Soyuz spacecraft was initially designed for rendezvous and docking operations in near earth orbit, leading to piloted circumlunar flight. |
| Soyuz A PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. Study 1962. Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system but with no base flange for a shroud. Equipment-engine section. |
| Soyuz ASTP PAO Russian manned spacecraft module. 4 launches, 1974.04.03 (Cosmos 638) to 1975.07.15 (Soyuz 19 (ASTP)). Soyuz 7K-OK basic PAO service module with pump-fed main engines and separate RCS/main engine propellant feed system. Equipment-engine section. |
 | Soyuz Kontakt Russian manned spacecraft. Cancelled 1974. Modification of the Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft to test in earth orbit the Kontakt rendezvous and docking system. |
 | Von Braun Landing Boat American manned Mars lander. Study 1952. The first design for a manned Mars lander based on engineering analysis. The enormous glider would have a wingspan of 153 m, and land on Mars horizontally either on skis, skids, or wheels on a prepared runway. |
 | Von Braun Lunar Lander American manned lunar lander. Study 1952. Von Braun's first lunar lander design was an immense spacecraft, larger in earth orbit than a Saturn V booster. |
 | Von Braun Passenger Ship American manned Mars orbiter. Study 1952. The first design for a manned Mars orbiter based on engineering analysis. 10 passengers would be housed in a 20-m-diameter sphere during the 963 day mission to Mars, in Mars orbit, and back to earth. |
Spacecraft:
Von Braun Cargo Ship,
Von Braun Passenger Ship,
Von Braun Lunar Lander,
Von Braun Landing Boat,
1956 Von Braun Passenger Ship,
1956 Von Braun Cargo Ship,
1956 Von Braun Landing Boat,
Soyuz A,
Soyuz A PAO,
Soyuz 7K-OK,
Soyuz 7K-OK PAO,
Soyuz Kontakt,
Salyut 1,
Soyuz 7KT-OK,
Soyuz 7K-OKS PAO,
Soyuz 7K-T,
Soyuz 7K-T PAO,
Salyut 4,
Soyuz 7K-TM,
Soyuz 7K-T/A9,
Soyuz ASTP PAO,
Soyuz 7K-MF6,
Soyuz 7K-MF6 PAO,
Progress,
Progress PAO.
Stages:
Von Braun 1948-1,
Von Braun 1948-2,
Von Braun 1948-3,
Von Braun 1952-1,
Von Braun 1952-2,
Von Braun 1952-3.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use
